We have spent many an hour mulling over how to exploit Moore’s Chasm theory.
But many, many more hours cursing the dynamics of the early market.
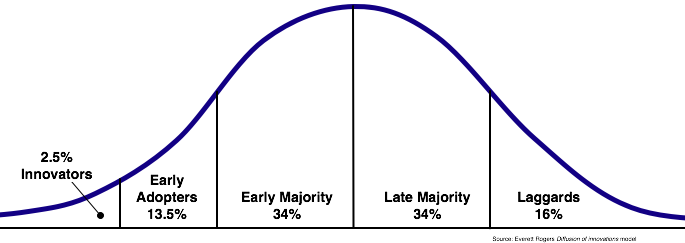
In particular, we wrestle with early adopters’ infatuation with all things new and their inability to stay loyal to ideas over time.
You see, the first buyers are often visionary in character, attracted by revolutionary change, comfortable with half-baked features and totally cool with the untested, unfinished.
They’re also needy, goal obsessed, and keen to brag. Especially about being the first on the block to grab innovation by the horns and wrestle it into submission.
They will always be among the first to quit.
Visionaries like to jump onto the next big thing. And that can be a problem. The early market is a dynamic, fickle force which can be hard to tame and even harder to keep caged.
Here are five things about the early market most overlook:
- The early market is always in the minority. If you talk to 100 people about your new product, only 10 will say it’s awesome. 90 will tell you it sucks. Or worse, they won’t even know it’s there. 90% rejection is hardly compelling evidence that you’re onto something.
- People who sell to the early market are rarely comfortable selling to the early market. Your team, those stalwarts who have chosen to join you on the front line of change, they too are surrounded by doubters and skeptics. So is your Board. And your investors. They want guarantees. Or at least promises. They will all push you to go for the money. Now. And the money lies in the fattest part of the Bell Curve with the elusive majority. So why aren’t you selling there now? Moore urges caution and the need to establish a beachhead first. But to do that is to sit back while someone else exploits the fat found in the middle of the herd!
- The early market is way different from the late market. To find where you are on the curve, it’s important to understand the differences between the two groups. Somewhere in your product’s journey to success is a gap. It lies between the radicalized, crazy, fanatical first-customers and their more prudent, careful, and risk-averse brethren. Pragmatists don’t trust visionaries. They think visionaries are crazy. And pragmatists bore visionaries with their endless prattling about avoiding risk and loading up your product with check-box features. Yet, significant numbers of pragmatists have to be swayed by visionaries for an idea to root and blossom.
- The traffic moves in one direction: from left to right, early to late. Ideas move from new to old. They are birthed. They grow. Mature. And eventually pass into the mainstream. And after a while they wither and die. The point here is that they rarely pass from mature to death and back to sexy again. Which means it can be hard for a new idea to retrace its steps, especially when the gloss has worn off.
- Your industry is not any different. Don’t fight the theory, embrace it. We have been teaching diffusion theory since Rogers first published Diffusion of Innovations in 1962 (check this out). It’s hardly a new idea or a novel expression of market development. The principles are tried and tested. Sure you can break into a market by penetrating the middle: but it takes a lot of money. That’s why so many Super Bowl advertisers are major, established brands — Coke, Pepsi, Jeep, Bud — and why so few companies trust debuting a novel idea in a $3 million commercial. So if you are outside the mainstream, you can gain a significant advantage by embracing the lessons of market adoption theory and watching your own customers for the telling signs of quivering, flighty pioneerdom. And even find ways to cross the chasm to that big, fat majority market. But more on that in another piece.
That’s how we see it. Join the conversation. #whatifmortar